speed of beta radiation|Characteristics of Beta Radiation / Particles : Cebu Henri Becquerel, while experimenting with fluorescence, accidentally found out that uranium exposed a photographic plate, wrapped with black paper, with some unknown Tingnan ang higit pa CheroCar Dash Mount Phone Holders Dashboard Cell Phone Holder for Jeep Wrangler JK JKU 2011-2017,Black. 18 4.8 out of 5 Stars. 18 reviews. Save with. Shipping, arrives in 2 days. Only 1 left. iOttie Easy One Touch 5 Universal Dashboard & Windshield Car Mount and Phone Holder.
speed of beta radiation,A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β decay and β decay, which produce electrons and . Tingnan ang higit paβ decay (electron emission)An unstable atomic nucleus with an excess of neutrons may undergo β decay, where a neutron is converted into a proton, an . Tingnan ang higit pa
Beta particles can be used to treat health conditions such as eye and bone cancer and are also used as tracers. Strontium-90 is the . Tingnan ang higit pa
Henri Becquerel, while experimenting with fluorescence, accidentally found out that uranium exposed a photographic plate, wrapped with black paper, with some unknown Tingnan ang higit pa• Common beta emitters• Electron irradiation• Particle physics• n (neutron) rays• δ (delta) rays Tingnan ang higit paOf the three common types of radiation given off by radioactive materials, alpha, beta and gamma, beta has the medium penetrating power and the medium ionising power. Although the beta particles given off by different radioactive materials vary in . Tingnan ang higit paBeta particles are moderately penetrating in living tissue, and can cause spontaneous mutation in DNA.Beta . Tingnan ang higit pa• Radioactivity and alpha, beta, gamma and Xrays• Rays and Particles University of Virginia Lecture Tingnan ang higit pa
Beta particles (β) are high energy, high speed electrons (β-) or positrons (β +) that are ejected from the nucleus by some radionuclides during a form of .When the beta particle moves faster than the speed of light (phase velocity) in the material, it generates a shock wave of electromagnetic radiation known as the Cherenkov radiation. The beta emission has a continuous spectrum. A 1 MeV .
When the beta particle moves faster than the speed of light (phase velocity) in the material, it generates a shock wave of electromagnetic radiation known as the Cherenkov radiation. .
The speed of the particles in beta rays is close to the speed of light. They have lower kinetic energy than alpha particles because although they have a high speed, they have .
The absorption properties of beta radiation make it useful in industrial and some medical applications. Experiments which deflect beta particles can measure their speed, which is . Typical \(\beta\) radiation can penetrate a few millimeters of tissue or about a meter of air. Beta radiation is thus hazardous even when not ingested. The range of \(\beta\)s .
The result for the decay constant is in which W0 is the maximum beta-particle energy in relativistic units ( W0 = 1 + Qβ / m0c2 ), with m0 the rest mass of the electron, c the .When the beta particle moves faster than the speed of light (phase velocity) in the material, it generates a shock wave of electromagnetic radiation known as Cherenkov radiation. Beta .Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by certain fission fragments or primordial radioactive nuclei such as potassium-40. The beta particles are a form of ionizing radiation, also known as beta rays.The production of beta particles is termed beta decay.There are two forms of beta decay, electron decay (β− decay) and positron decay (β+ . Radiation Basics. Radiation is energy given off by matter in the form of rays or high-speed particles. All matter is composed of atoms.Atoms are made up of various parts; the nucleus contains minute particles called protons and neutrons, and the atom's outer shell contains other particles called electrons.The nucleus carries a positive electrical charge, while the .
Beta Radiation. Beta radiation consist of free electrons or positrons at relativistic speeds.These particles are known as the beta particles. Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by .Revision notes on 8.1.3 Alpha, Beta & Gamma Radiation for the AQA A Level Physics syllabus, written by the Physics experts at Save My Exams.Beta Particles Description Beta Particles. Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by certain fission fragments or certain primordial radioactive nuclei such as potassium-40. The beta particles are a form of ionizing radiation, also known as beta rays.The production of beta particles is termed beta decay.There are two forms of beta decay, electron .
By 1902, it was recognized that \(\beta\) radiation is the emission of an electron. Although \(\beta\)s are electrons, they do not exist in the nucleus before it decays and are not ejected atomic electrons—the electron is created in the nucleus at the instant of decay. . The speed at which they travel is the other major factor affecting the .
Both alpha particles and beta particles produce ionizing radiation. The charge they carry can remove electrons from atoms. . Each alpha particle has two protons and two neutrons. A beta particle can be a high speed electron or positron (© 2019 Let’s Talk Science). Neutrons are particles located in the nucleus of an atom. Unlike protons and .

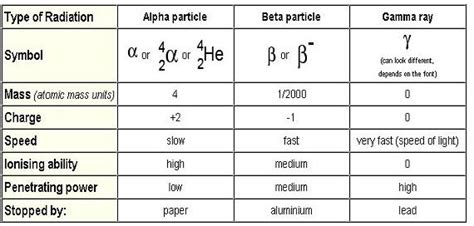
Alpha (α) radiation consists of a fast-moving helium-4 (4He) nucleus and is stopped by a sheet of paper. Beta (β) radiation, consisting of electrons, is halted by an aluminium plate.Gamma (γ) radiation, consisting of energetic photons, is eventually absorbed as it penetrates a dense material.Neutron (n) radiation consists of free neutrons that are blocked by light elements, like .Alpha (α) radiation consists of a fast-moving helium-4 (4He) nucleus and is stopped by a sheet of paper. Beta (β) radiation, consisting of electrons, is halted by an aluminium plate.Gamma (γ) radiation, consisting of energetic photons, is eventually absorbed as it penetrates a dense material.Neutron (n) radiation consists of free neutrons that are blocked by light elements, like .speed of beta radiationBeta Particles. Beta (β −) particles are high energy electrons emitted from the nucleus. β − particles are emitted by nuclei that have too many neutrons; Beta is a moderately ionising type of radiation . This is due to it having a charge of +1e; This means it is able to do some slight damage to cells (less than alpha but more than gamma)
The second kind of radiation is a beta particle. It's an electron that is not attached to an atom. It has a small mass and a negative charge. Tritium, which is produced by cosmic radiation in the atmosphere and exists all around us, emits beta radiation. Carbon-14, used in carbon-dating of fossils and other artifacts, also emits beta particles.
The beta decay is a radioactive decay in which a proton in a nucleus is converted into a neutron (or vice-versa). In the process the nucleus emits a beta particle (either an electron or a positron) and quasi-massless particle, the neutrino. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Beta decay schematics (CC BY-NC-ND; Paola Cappellaro)
10 Important Properties of Beta Particles. Property 1: Beta particles (β – particles) are fast-moving electrons or positrons with high energy emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus. Property 2: Penetrating power of beta particles is higher than α-particles. They can penetrate through a thin metal foil. Beta radiation consists of an electron and is characterized by its high energy and speed. Beta radiation is more hazardous because, like alpha radiation, it can cause ionisation of living cells. Unlike alpha radiation, . Beta Radiation. Beta radiation consist of free electrons or positrons at relativistic speeds.These particles are known as the beta particles. Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by certain fission fragments or by certain primordial radioactive nuclei such as potassium-40. The beta particles are a form of ionizing radiation .

Radioactivity - Beta Decay, Nuclear Reactions, Radiation: The processes separately introduced at the beginning of this section as beta-minus decay, beta-plus decay, and orbital electron capture can be appropriately treated together. They all are processes whereby neutrons and protons may transform to one another by weak interaction. In striking contrast to .Characteristics of Beta Radiation / Particles Similarly, if a neutron is converted to a proton, it is known as β- decay. In beta plus decay, the proton disintegrates to yield a neutron causing a decrease in the atomic number of the radioactive sample. Login. Study Materials. NCERT Solutions. NCERT Solutions For Class 12. . The beta particle is a high-speed electron when it is a .
speed of beta radiation Characteristics of Beta Radiation / Particles Beta Radiation. Michael F. L'Annunziata, in Radioactivity, 2007. 2.1 INTRODUCTION. . Charged particles, such as beta particles, that possess sufficient energy can travel at a velocity exceeding the speed of light in media such as water, organic solvents, plastic, and glass. When this occurs, the charged particle will produce Cherenkov photons . Beta radiation. Beta radiation occurs when an atom decays by giving off a high-energy, high-speed particle that has a negative or positive charge. These “beta” particles are both smaller and more energetic than alpha particles. There are two types of beta decay. When a negatively charged particle is emitted from the nucleus, it is called .
speed of beta radiation|Characteristics of Beta Radiation / Particles
PH0 · Radioactivity
PH1 · Characteristics of Beta Radiation / Particles
PH2 · Beta radiation: range and stopping
PH3 · Beta particles
PH4 · Beta particle
PH5 · Beta decay: what are beta particles and beta radiation types
PH6 · Beta Radiation
PH7 · Beta Particles
PH8 · 31.1: Nuclear Radioactivity